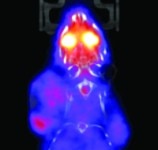
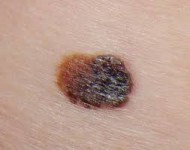
Ribosome Fingerprints to help Cancer Diagnosis
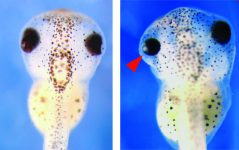
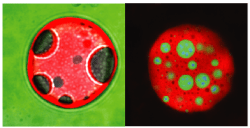
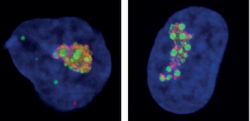
In an amazing collaboration with the Eva Maria Novoa Lab (CRG, Barcelona, Spain), … Milenkovic et al. demonstrate that rRNA modifications are differentially modified across tissues, developmental stages, and in disease. The authors show that rRNA modification patterns, also termed “epitranscriptomic rRNA fingerprints” are sufficient to accurately identify tissue of…